Tag สำหรับ JSP ที่ใช้มีดังนี้
scriptlet - <% ... %> เป็นพื้นฐานของ JSP เลย เราสามารถเขียน code java ลงไปในนี้ได้
XML-compliant ที่ใช้แทน <% list.add("Fred"); %> จะเป็นดังนี้
<jsp:scriptlet>
list.add("Fred");
</jsp:scriptlet>
directive - <@% ...%>
| Directive | Attribute | Usage |
|---|---|---|
page | contentType | กำหนดการเข้ารหัสตัวอักษรหรือ MIME type ของ response ในกรณีที่ไม่ได้กำหนดค่าจะใช้ค่าจาก pageEncoding attribute default = "text/html;charSet=ISO-8859-1" |
import | import class อื่นเข้ามาใช้งาน XML-compliant: <jsp:directive.page import="path/file" /> | |
isThreadSafe | ถ้าเป็น "true" แปลว่า Servlet ที่ได้ หลังจาก translate JSP แล้วจะ implement SingleThreadModel เพื่อให้ Servlet เป็น thread safe (ซึ่งการทำงานจริงๆ ของ SingleThreadModel ขึ้นอยู่กับ Web Container แต่ละเจ้า จะ implement เป็นแบบไหน ซึ่งโดยลึกๆ แล้ว ไม่ค่อยได้ประโยชน์เท่าไร) | |
errorPage | url ของ exception page | |
isErrorPage | บอกให้รู้ว่า JSP page ปัจจุบันเป็น errorPage หรือไม่ ถ้าเป็น "true" ก็จะมี implicit object exception ถ้าเป็น "false" ก็จะไม่สามารถใช้ object exception ใน page นี้ได้default = "false" | |
isELIgnored | บอกว่าจะไม่สามารถใช้ Expression Language ใน JSP นี้ได้ | |
language | define scripting language ที่ใช้ใน scriptlet และ declaration default = Java | |
extends | กำหนด class ที่ JSP นี้จะ extend ซึ่งโดยปกติ จะึขึ้นอยู่กับ web containner ดังนั้นถ้าเราต้องการจะ extend ตัวอื่นจะต้องกำหนดไว้ แต่ควรจะแน่ใจจริงๆ ว่ามันทำงานได้นะจ๊ะ | |
session | กำหนดว่าเอกสารนี้จะใช้ implicit object session หรือไม่ สามารถกำหนดเป็น session="false" ถ้าไม่ต้องการใช้ sessiondefault = "true" | |
buffer | ควบคุมการใช้ buffer สำหรับ jsp ว่าต้องการ buffer หรือไม่ ค่าเริ่มต้นจะอยู่ที่ 3 KB | |
autoFlush | เมื่อ buffer เต็มจะ cleart buffer ให้อัตโนมัติ default = "true" | |
info | สามารถกำหนดเป็นค่า string ใดๆ ซึ่งจะเก็บไว้ใน servlet ที่ได้ translate จาก JSP และสามารถดึงขึ้นมาโดย Servlet.getServletInfo() | |
pageEncoding | บอกว่า page JSP encode ด้วยรหัสอะไร ในกรณีที่ไม่กำหนดค่าจะใช้ค่าจาก contentType attribute default = " ISO-8859-1" | |
include | file | ชื่อไฟล์ที่ต้องการนำมา include (ไฟล์ servlet ที่ได้จะเสมือนเอา included file มาแปะไว้กับ servlet เลย) |
taglib | tagdir | directory ที่เก็บ tag file ไว้ (จะใช้ในกรณีที่ไม่ได้ declare tag file ไว้ใน tld) |
prefix | ชื่อที่ใ้ช้ในการเรียก tag lib นี้ ซึ่งเป็นค่าอะไรก็ได้ ยกเว้น jsp, jspx, java, javax, servlet, sun, sunw | |
uri | ชื่อที่ต้องใช้ให้ตรงกับไฟล์ Tag Library Descriptor (TLD) | |
tag*ใช้สำหรับ tag file เท่านั้น | import | import class อื่นเข้ามาใช้งาน |
isELIgnored | บอกว่าจะไม่สามารถใช้ Expression Language ใน JSP นี้ได้ | |
language | define scripting language ที่ใช้ใน scriptlet และ declaration default = Java | |
body-content | มีค่าได้ดังนี้
| |
dynamic-attributes | ชื่อของ dynamic attribute ซึ่งจะรับเป็น HashMap เป็นชื่อและค่าของ attribute | |
attribute | name | ชื่อของ attribute ที่รับเข้ามา |
required | เป็นค่า boolean เพื่อบอกว่าเป็น attribute ที่ต้องมีเสมอหรือไม่ | |
rtexprvalue | ค่า boolean ที่บอกว่าจะ สามารถรับเป็น scriptlet ได้หรือไม่ | |
variable*ใช้สำหรับ tag file เท่านั้น | name-given | ชื่อของตัวแปร |
variable-class | class ของตัวแปร เช่น java.lang.String |
expression - <%= ... %> ใช้แทน out.print() ในการแสดงผล
XML-compliant ที่ใช้แทน <%= it.next %> จะเป็นดังนี้
<jsp:expression>
it.next()
</jsp:expression>
declaration - <%! ... %> ใช้สำหรับ declare instance variable หรือ method
XML-compliant ที่ใช้แทน <%! int y = 3; %> จะเป็นดังนี้
<jsp:declaration>
int y = 3;
</jsp:declaration>
XML-compliant คือการทำให้ JSP page เป็น JSP document ความแตกต่างของสองอันนี้ก็คือ JSP document จะเป็น XML-compliant คือเป็น well-formed XML ซึ่งโดยปกติแล้ว เราจะไ่ม่ได้เขียน JSP document เอง แต่อาจจะใช้ tools ในการสร้างขึ้นมา ตัวอย่างอีก ตัวอย่างหนึ่งสำหรับ XML-compliant ก็คือการเขียน text บน JSP page ซึ่งจะใช้ตัวอย่างด้านล่างแทน
<jsp:text>
This is text.
<jsp:text>
สำหรับ comment สามารถใช้ comment ใน html คือ <!-- comment --> หรือใช้ JSP comment <% /* comment */ %> ก็ได้ แต่ถ้าใช้ html comment ข้อความก็จะถูกส่งไปที่ client เสมือนกับ html comment ทั่วไป แต่สำหรับ JSP comment จะถูกตัดทิ้งไปเมื่อ translate จาก JSP เป็น Servlet
JSP Implicit Object
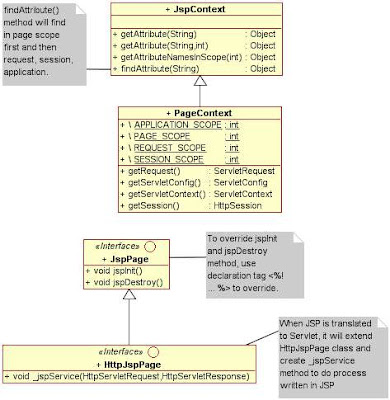
| API | Implicit Object | Used by Servlet |
|---|---|---|
| JspWriter | out | response.getWriter()* * it will get PrintWriter, not JspWriter |
| HttpServletRequest | request | request* * depend on how to declare parameter name in service method |
| HttpServletResponse | response | response* * depend on how to declare parameter name in service method |
| HttpSession | session | request.getSession() |
| ServletContext | application | getServletContext() |
| ServletConfig | config | getServletConfig() |
| Throwable | exception | |
| PageContext | pageContext | N/A |
| Object | page | N/A page scope is not available in Servlet |
tag file ก็สามารถใช้ implicit object ตัวเดียวกับ JSP file ได้เหมือนกัน ยกเว้น ServletContext ซึ่งใน tag file จะใช้เป็น jspContext ซึ่งเป็น JspContext object แทน และไม่สามารถใช้ application ซึ่งเป็น ServletContext object ได้
EL Implicit Object
| Implicit Object | Used by Scriplet |
|---|---|
| ${pageScope.name} | N/A page scope is not available in Servlet |
| ${requestScope.name} | request.getAttribute("name") |
| ${sessionScope.name} | session.getAttribute("name") |
| ${applicationScope.name} | application.getAttribute("name") |
| ${param.name} | request.getParameter("name") |
| ${paramValues.name[index]} | request.getParameterValues("name")[index] |
| ${header.name} | request.getHeader("name") |
| ${headerValues.name[index]} | Enumeration headers |
| ${cookie.name} | Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); |
| ${initParam.name} | application.getInitParameter("name") |
| ${pageContext.name} | pageContext.getName() เช่น pageContext.exception ซึ่งเป็นตัวแปรเดียวกับ exception ใน JSP Implicit Object ซึ่งจะสามารถ access ตัวแปรนี้ได้จะต้องกำหนดให้* <%@ page isErrorPage="true" %> *แต่ไปลองดูแล้วกับ Tomcat 6, Servlet 2.5 ปรากฎว่าถึงไม่ใส่ ก็สามารถ access ตัวแปรได้นะ ไม่แน่ใจเหมือนกัน |
ซึ่ง pageScope, requestScope, sessionScope, applicationScope สามารถละไว้ได้ถ้าในกรณีที่เราไม่ต้องการระบุว่าจะใช้ attribute จาก scope ใด
${requestScope.person.name} --> ${person.name}
ยกเว้นถ้าในกรณีที่มี attribute ชื่อเดียวกันในหลาย scope และต้องการระบุว่าต้องการจาก scope ไหน หรือในกรณีที่ชื่อของ attribute ไม่เป็นไปตาม Java naming rule เช่น
request.setAttribute("foo.person", p); // ซึ่ง เราไม่สามารถใช้ ${foo.person.name} ได้
${requestScope["foo.person"].name}
EL Operation
Arimetic uses + , - , *, / or div, % or mod
Logical uses && or and, || or or, ! or not
Relational uses == or eq, != or ne, < or lt, > or gt, <= or le, >= or ge
EL Function
ใช้การกำหนด function ใน Tag Library Descriptor (TLD) file โดยเรียก public static method ใน class
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<taglib version="2.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-jsptaglibrary_2_0.xsd ">
<tlib-version>1.2</tlib-version>
<short-name>NMTOKEN</short-name>
<uri>DiceFunction</uri>
<function>
<name>rollIt</name>
<function-class>com.amadmonster.scwcd.el.function.DiceRoller</function-class>
<function-signature>int rollDice()</function-signature>
</function>
<!-- สำหรับ function ที่รับตัวแปร -->
<function>
<name>rollWith</name>
<function-class>com.amadmonster.scwcd.el.function.DiceRoller</function-class>
<function-signature>int rollDice(int)</function-signature>
</function>
</taglib>
นอกจาก tld file จะประกอบด้วย EL Function แล้วยังสามารถใส่ custom tag ด้วย แต่จะกล่าวในตอน JSTL & Custom Tag ต่อไป
Standard Action
| Action | Attribute | Usage |
|---|---|---|
jsp:useBean | id | เป็น identifier ของ object โดยรับเป็น string name ของ JavaBean นั้นๆ ซึ่งจะแปลเป็น servlet โดยใช้ getAttribute หรือ setAttribute method ดังนั้นจึงเป็น case sensitive |
scope | เป็น scope ที่ใช้ในการอ้างอิงถึง JavaBean นั้น มีค่าได้ดังนี้
default: page | |
class | class ของ bean ที่จะถูกสร้างขึ้นในกรณีที่ attribute นั้นๆ ไม่มีอยู่ใน scope ที่ ซึ่งไ่ม่สามารถกำหนดเป็น interface หรือ abstract class ได้ property นี้เป็น optional คือไม่จำเป็นต้องมีก็ได้ ซึ่งใช้ในกรณีที่เราต้องการดึงค่า attribute ขึ้นมาใช้ แต่ในกรณีที่ไม่มี attribute อยู่จะทำการสร้าง bean เพื่อจะ add attribute ก็จะ error InstantiationException | |
type | Type ของ bean ในกรณีที่จะถูกสร้างขึ้น เมื่อไม่มีอยู่ใน scope ซึ่งอาจจะเป็นค่าเดียวกับ class property หรือว่าเป็น parent object ของ class property หรือว่าเป็น interface ก็ได้ในกรณีที่ไม่ได้กำหนด จะถือว่าเป็นค่า default คือ เหมือนกับ class | |
beanName | ชื่อของ Bean | |
jsp:setPropertyสามารถใส่ไว้ใน body ของ jsp:useBean ได้ กรณีที่ต้องการให้ set property เมื่อมีการสร้าง bean ใหม่ (ในกรณีที่มีอยู่แล้วจะไม่ set) | name | ชื่อของ Bean (เป็นค่า property id ใน action jsp:useBean นั้นเอง) ที่เรา้้จะ set ค่า |
property | ชื่อ property ที่เราต้องการจะ set ค่า ถ้าให้ค่าเป็น "*" คือ ให้ map ชื่อ property กับ parameter ของ request object ที่ชื่อตรงกัน | |
value | ค่าที่จะ set ใหักับ property นั้นๆ (ถ้ามีการ set ค่าใช้กับ param attribute ก็จะต้องไม่มีการ set ค่ากับ value อีก | |
param | ชื่อ parameter ที่จะให้ค่ากับ property นั้นๆ ในกรณีนี้จะไม่ใส่ property value หรือในกรณีที่ไม่ใส่ัทั้ง value และ param แสดงว่า param เป็นค่าเดียวกับ property (หรือให้ใช้ param ที่มีค่าเดียวกับ property สำหรับ set ค่า) | |
jsp:getProperty | name | ชือของ object Bean (ค่า property id ใน action jsp:useBean นั้นเอง) ที่เราต้องการจะรับค่า |
property | property ที่เราต้องการจะรับค่า | |
jsp:forward | page | relative url ที่ต้องการ forward ไป ซึ่งจะเป็น JSP, servlet หรือ dynamic file อื่นๆ ก็ได้ ที่อยู่ใน application เดียวกัน |
jsp:include | page | relative url ที่จะ include (jsp:include ให้ผลเหมือนกับ directive include แต่ว่าจะทำเมื่อ runtime สำหรับในกรณีที่ included file ยังมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงอยู่) |
jsp:param | name | ชื่อตัวแปรที่ต้องการ forward ไปพร้อมกับ jsp:forward หรือ jsp:include เช่น<jsp:include page="Header.jsp"> |
value | ค่าของตัวแปรตามชื่อที่ต้องการส่ง | |
jsp:attribute | name | ชื่อของ attribute ซึ่งตัวนี้มี body ด้วยเป็นค่าของ attribute เช่น<jsp:attribute name="user">${userName}</jsp:attribute>jsp:attribute สามารถใส่ใน custom tag body ได้ ถึงแม้ว่าจะกำหนด <body-content>empty</body-content> |
jsp:doBody*ใช้สำหรับ tag file เท่านั้น | สำหรับ tag file เพื่อดึงค่า body ของ tag |
Reference:
JSP 2.0 Syntax Reference
No comments:
Post a Comment